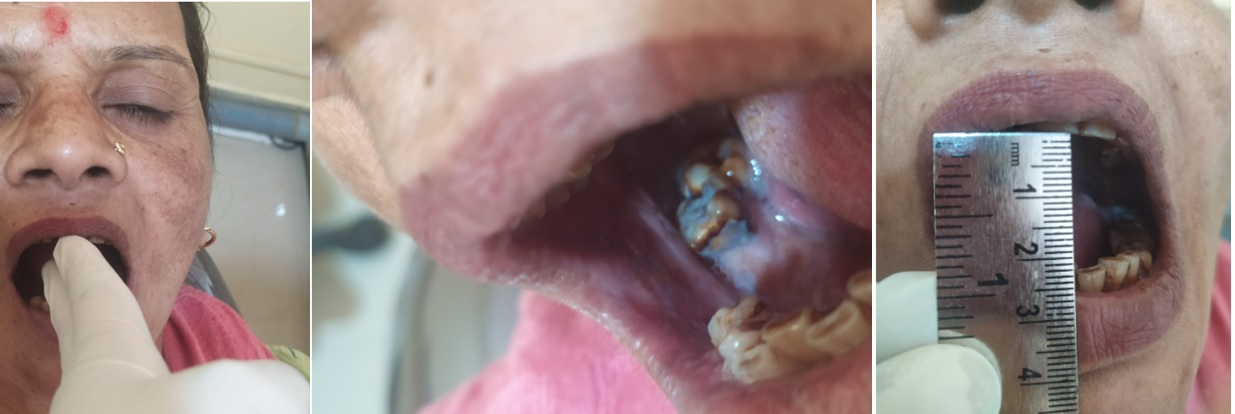
Oral submucous fibrosis (OSMF) is a chronic, progressive, and potentially malignant condition that affects the oral mucosa, particularly the buccal mucosa (inner lining of the cheeks). OSMF is prevalent in Southeast Asian countries, particularly in India, where it is a major public health concern. It is primarily associated with the habit of chewing areca nut, which is commonly mixed with tobacco and various other ingredients and is commonly consumed in South Asia. Areca nut contains alkaloids such as arecoline, which are known to cause fibrosis in the oral cavity. It is characterized by the formation of fibrous bands in the sub mucosal layer of the oral cavity leading to reduced mouth opening, difficulty in swallowing and speech, and a burning sensation in the mouth.
The most commonly accepted etiological factor for OSMF is the use of areca nut, which is widely consumed in the form of chewing tobacco and other forms of smokeless tobacco. Other risk factors for OSMF include nutritional deficiencies, chronic irritation of the oral mucosa, and viral infections. The disease has a long latency period and can take years to manifest. . The main pathological feature of OSMF is the deposition of excessive fibrous tissue in the sub mucosal layer of the oral cavity, leading to reduced mouth opening, difficulty in chewing and swallowing, and progressive stiffness of the oral tissues.
The diagnosis of OSMF is usually made clinically based on the history, symptoms, and physical examination. A biopsy may be required in cases where the diagnosis is uncertain or to rule out malignancy. Treatment of OSMF is primarily aimed at relieving symptoms and preventing disease progression. Early intervention is important to prevent irreversible damage to the oral mucosa.
The symptoms of OSMF typically include a burning sensation in the mouth, dryness, progressive restriction of mouth opening (trismus), and the development of fibrous bands in the oral cavity. In advanced stages, OSF can lead to difficulty in eating, speech impairment, and an increased risk of oral cancer.
Treatment of OSMF focuses on relieving symptoms, preventing disease progression, and reducing the risk of malignant transformation. Treatment options include the use of corticosteroids, surgical excision of fibrous bands, intralesional injections, tissue reconstruction and physical therapy. The use of antioxidants and other drugs to prevent disease progression has also been studied. Prevention of OSMF is based on avoiding the use of areca nut and other forms of smokeless tobacco, maintaining good oral hygiene, and a healthy diet.
Early diagnosis and intervention are important to prevent irreversible damage to the oral mucosa, and prevention is based on avoiding the use of areca nut and other forms of smokeless tobacco, maintaining good oral hygiene, and a healthy diet.
It's important to consult with a healthcare professional or a dentist for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan if you suspect you may have oral submucous fibrosis. They will be able to provide you with the most up-to-date and accurate information based on your specific situation.
Our Doctors
SMILE IN MINUTES Dental Care Doctors

Dr. Priyanka
Sr. Dental Surgeon

Dr. Mowmita Barik
Dental Surgeon (BDS)

Dr. Sapna
Dental Surgeon (BDS)

Dr. Md. Shoaib
Dental Surgeon (BDS)

Dr. Rubiya
Dental Surgeon (BDS)

Dr. Kuldeep
Dental Surgeon (BDS)

Dr. Ribhu
Dental Surgeon (BDS)

Dr. Sonam Tonger
Dental Surgeon (BDS)

Dr. Chanderalata
Dental Surgeon (BDS)

Dr. Neha
Dental Surgeon (BDS)

Dr. Priyanka Arora Sethi
Dental Surgeon (BDS)