Pregnancy is an exciting time in a woman's life, but it can also come with its own set of challenges, including dental issues. Dental issues during pregnancy are not uncommon and can range from mild to severe. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can increase the risk of developing gum disease, tooth decay, and other dental problems.
How pregnancy affects oral health - Hormonal changes during pregnancy can lead to changes in the mouth, including increased blood flow and inflammation of the gums.
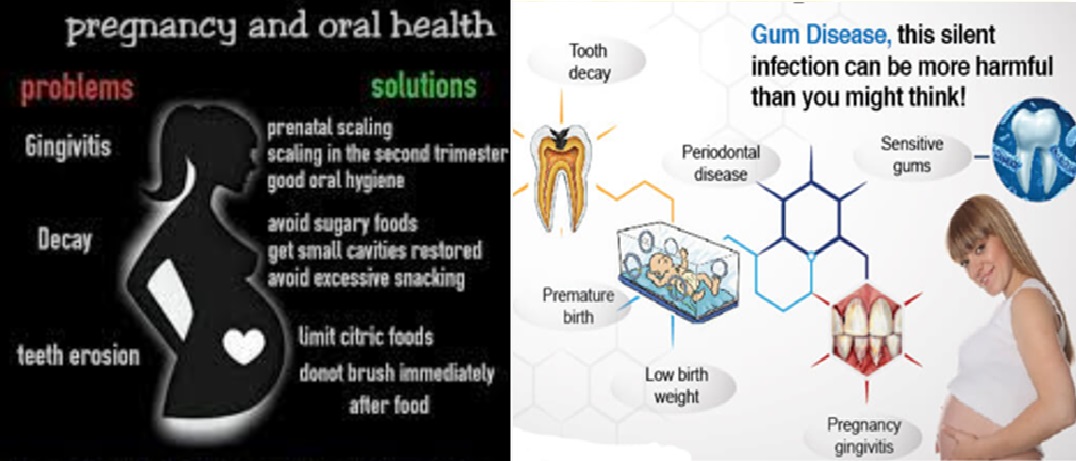
Gum disease - Pregnant women are more susceptible to gum disease due to hormonal changes that can make the gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation. Proper oral hygiene, such as brushing and flossing regularly, and regular dental cleanings can help prevent and treat gum disease.
Gingivitis: Gingivitis is a common condition during pregnancy. Hormonal changes can cause an increase in the production of plaque, which can lead to inflamed and bleeding gums. Pregnant women should brush twice a day and floss daily to prevent gingivitis. If the condition persists, a visit to the dentist may be necessary.
Tooth decay - Pregnant women may be at increased risk of tooth decay due to changes in eating habits and morning sickness that can expose the teeth to more acid. Maintaining a healthy diet and oral hygiene can help prevent tooth decay.
Pregnancy tumors: Pregnancy tumors are small, non-cancerous growths that may develop on the gums during pregnancy. They are often found in the second trimester and can be caused by hormonal changes. Pregnancy tumors typically go away on their own after delivery, but if they cause discomfort or interfere with eating or speaking, they can be removed by a dentist.
Dry mouth: Dry mouth is a common complaint during pregnancy, and it can be caused by hormonal changes or dehydration. Drinking plenty of water and avoiding sugary and caffeinated drinks can help prevent dry mouth. Women can also try chewing sugar-free gum or sucking on sugar-free candies to stimulate saliva production.
Enamel erosion: Acidic foods and drinks can cause enamel erosion, which can lead to tooth sensitivity and decay. Pregnant women should limit their consumption of acidic foods and drinks and wait at least 30 minutes after eating or drinking before brushing their teeth to prevent further enamel erosion.
Morning sickness: Nausea and vomiting during pregnancy can lead to enamel erosion and tooth decay. To protect your teeth, try rinsing your mouth with water or a fluoride mouthwash after vomiting and wait at least 30 minutes before brushing.
Emergency dental care: In some cases, pregnant women may require emergency dental care. It is important to inform the dentist that you are pregnant so that they can take the necessary precautions. Dental procedures such as X-rays and certain medications may need to be avoided during pregnancy.
Dental treatments during pregnancy - Some dental treatments, such as X-rays and certain medications, may need to be postponed until after the baby is born to ensure the safety of both the mother and the fetus.
The risks of dental problems during pregnancy - Gum disease and tooth decay can increase the risk of preterm labor and low birth weight, making it important to address any dental issues as soon as possible.
In conclusion, maintaining good oral health during pregnancy is essential for the health of both the mother and the baby. Pregnant women should continue to practice good oral hygiene, eat a balanced diet, and visit their dentist regularly to prevent and manage any dental issues that may arise. Eating a healthy diet can help promote good oral health during pregnancy and support the development of a healthy baby.
Our Doctors
SMILE IN MINUTES Dental Care Doctors

Dr. Priyanka
Sr. Dental Surgeon

Dr. Mowmita Barik
Dental Surgeon (BDS)

Dr. Sapna
Dental Surgeon (BDS)

Dr. Md. Shoaib
Dental Surgeon (BDS)

Dr. Rubiya
Dental Surgeon (BDS)

Dr. Kuldeep
Dental Surgeon (BDS)

Dr. Ribhu
Dental Surgeon (BDS)

Dr. Sonam Tonger
Dental Surgeon (BDS)

Dr. Chanderalata
Dental Surgeon (BDS)

Dr. Neha
Dental Surgeon (BDS)

Dr. Priyanka Arora Sethi
Dental Surgeon (BDS)